Grief is a universal and highly personal experience. It can be caused by anything from the loss of a loved one, a major life transition, or even ending a relationship. In any case, grieving always affects us emotionally and sometimes even physically. At times, it can also be a difficult, if not overwhelming, experience.
At Excel Behavioral Health, we care about you and are committed to supporting you through the grieving process. In this article, we’ll help you learn about and understand what the grieving process is, the stages of grief, and what factors can influence how you grieve. We’ll also tell you how to know when to get help for grief because you do not have to experience it alone.
What Is the Grieving Process?
Grief is a natural and emotional response to significant loss. When experiencing grief, we often feel a range of emotions, from sadness, anger, guilt, confusion, or even relief. People usually associate grief with the death of someone they love, but it can also result from other life-altering circumstances, such as divorce, job loss, or even a major illness.
It’s essential to remember that grieving is not a linear process, and it varies from person to person. Not everyone will progress through the stages in the same order or at the same rate. But if you know what to expect, it may be easier to process the events and emotions that you experience during the grieving process.
The 5 Stages of the Grieving Process
Many experts define the grieving process as consisting of five distinct stages. The most well-known model is the Five Stages of Grief, developed by Elisabeth Kübler-Ross. These stages of grief are not necessarily linear; some people may move back and forth between stages.
1. Denial
In the first stage of grief, the loss is often met with shock and denial. No one is ever fully prepared for such a devastating event, so the first reaction to loss is that it’s not real. A person in grief often describes it as “feeling like in a fog”, and this stage is commonly associated with emotional numbness.
2. Anger
After shock and denial subside, anger may quickly set in. Once a person realizes that the loss is real and cannot be avoided, it is very common to become angry. During the anger stage of grief, a person might feel a need to know why this happened to them and ask the question: “Why me?” Anger may be directed towards themselves, the person they lost, or other people or situations.
3. Bargaining
The bargaining stage of grief is a mental strategy that a person often uses to come to terms with a situation. When a person is overwhelmed by grief and despair, they may think of what they could’ve done differently in order to prevent the loss. They might have a number of “what ifs” and “if only” scenarios going through their head. This stage of grief is essentially a coping mechanism that provides temporary relief.
4. Depression
Depression, or deep sadness, is one of the most well-known stages of grief. A person who has moved on from denial, anger, and bargaining may finally allow themselves to fully feel the depth of their loss. This can result in depression, a heavy feeling of sadness, lack of motivation, and even hopelessness. Crying, feeling tired or numb, and a lack of focus are some of the most common symptoms associated with this stage of grief.
5. Acceptance
The last stage of grief is acceptance. As the name suggests, a grieving person in this stage may have come to terms with the loss. It’s important to note that this does not mean that the loss is no longer felt as deeply as before. The acceptance stage of grief means a person has accepted the reality of the loss and their new situation and has developed the tools to move on with their life.
Factors That Impact the Grieving Process
Even though these five stages of grief can be expected, the grieving process can still look different for each person. There are many reasons that can influence the intensity of a person’s experience with grief.
Some of those factors include:
- Your Relationship to the Loss – The closer a person is to the source of grief, whether that is another person or a life situation, the more likely they are to experience stronger emotions.
- Coping Skills and Emotional Resilience – A person’s ability to cope with the emotional pain of loss can significantly impact the grieving process.
- Social Support – Having friends, family, or support groups can help a person go through grief more easily and quickly.
- Mental Health History – Having preexisting anxiety or depression disorders can also significantly affect how a person copes with loss.
- Cultural or Religious Beliefs – It’s not uncommon for culture and faith to play a significant role in grieving, particularly in healing and traditional beliefs.
When to Get Help for the Grieving Process
Grieving is a natural and normal response to loss, but sometimes it can get in the way of a person’s ability to function normally. It’s important to know when to get help for grief to avoid developing or worsening your mental health issues.
Here are a few of the most common signs that you or someone you know might need outside help with grief:
- Feeling “Stuck” in Grief – Sadness, anger, anxiety, or other feelings related to loss can feel never-ending sometimes. When feelings of grief do not improve or pass over a long period of time, this can often be a sign of complicated grief. Complicated grief is a condition in which the normal process of grieving is prolonged, and the pain of a person’s loss does not ease over time.
- Difficulty Performing Basic Life Tasks – Eating, sleeping, working, and taking care of yourself are some of the most important daily functions that you may struggle to do when in prolonged grief.
- Withdrawing from Others – Grief can often lead to isolation and avoidance of friends and family; however, this behavior is not healthy and can be easily improved by seeking professional help.
- Recurring Guilt or Self-Blame – Intense feelings of guilt and self-blame are not a healthy part of the grieving process and can be very damaging to one’s mental well-being.
- Suicidal Thoughts – If grief leads a person to feel as if life is not worth living, it’s extremely important to seek help immediately.
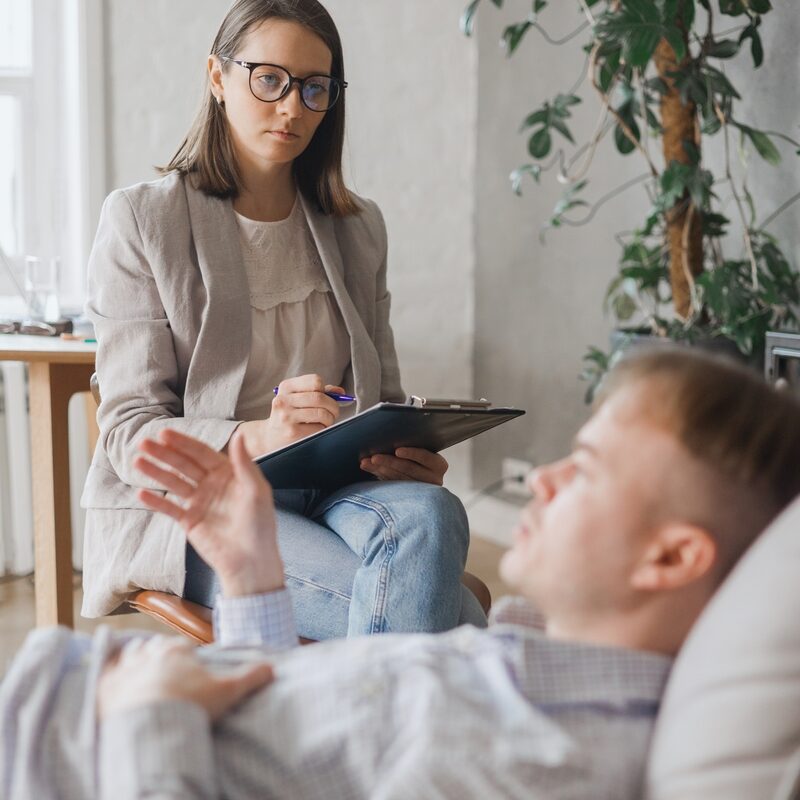
How Excel Behavioral Health Can Help You Through Grief
At Excel Behavioral Health, we understand that the death of a loved one or other forms of loss can be extremely hard to deal with. If you’ve been feeling down and unable to move on, we are here to provide you with support, guidance, and expert care.
We offer a range of therapy services and create personalized treatment plans tailored to your specific needs. Our experts can help you move on from prolonged grief, deal with anxiety, depression, and a number of other mental health issues related to loss.
Some of our services include:
- Individual and group therapy allow you to share your grief with others.
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) to help change your negative thought patterns.
- Mindfulness to help you take control of your overwhelming emotions.
- Trauma therapy for dealing with grief-related trauma.
Contact Excel Behavioral Health Today
Grief is a difficult yet natural process that we all must go through at some point in life. If you or someone you love is experiencing the grieving process, it’s important to understand that you do not have to experience it alone. At Excel Behavioral Health, we are here to help you navigate this challenging time and provide you with high-quality care.
Contact us today to learn more about our services and various therapy options, speak with one of our specialists, or schedule a consultation. Let us help you find hope after loss and move on to a better tomorrow. Call or reach out to us online now, because you are not alone, and we care about you.